Good casting properties, high resistance to corrosion, electronic and thermal conductivity - due to these properties, non-ferrous metals are often used in the electrical and construction industries, but also for the production of coins. Euro coins, for example, consist of a copper-nickel alloy in the middle, while the gold-colored edge is made of brass. Brass, in turn, is an alloy of copper with zinc. Some valuable bullion coins also contain non-ferrous metal, mainly copper. But what exactly are non-ferrous metals?
The definitions
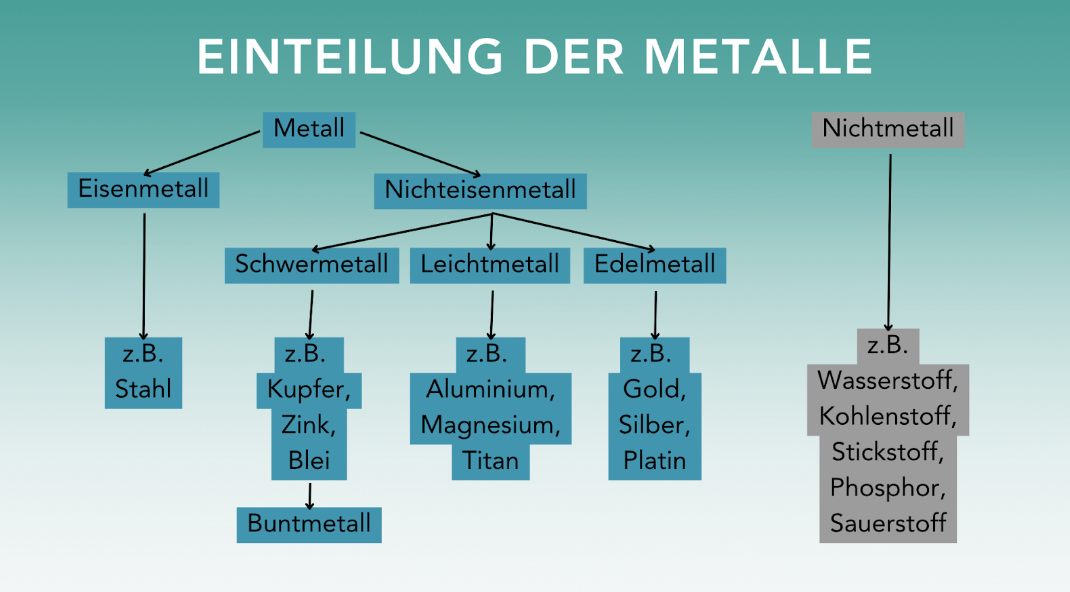
Two definitions are commonly used for the term "non-ferrous metal". On the one hand, the term stands for all metals except iron. The typical non-ferrous metals cadmium, cobalt, copper, nickel, tin and zinc therefore belong to the group of non-ferrous metals. However, precious metals such as silver and gold are not included. The term "non-ferrous metal" refers to the color of the metal or the color of the alloy - bronze and brass are therefore also non-ferrous metals. On the other hand, the definition includes all base metals (except iron) that form colored ores with non-metals - such as oxygen - and therefore have a "color". This is also the reason why precious metals are not counted as non-ferrous metals: Precious metals (such as gold and silver) are metals that hardly react with non-metals and therefore do not form (colored) ores.